Ovarian Cyst Surgery
Your Ovarian Cyst Surgery in Tunisia at an Affordable Price
Opt for a medical stay with Tunisia Destination Santé and benefit from the expertise of our specialist doctors and the best healthcare facilities in Tunisia. Thanks to our tailor-made service, you will benefit from complete support in a secure and comfortable setting.
How does it work?
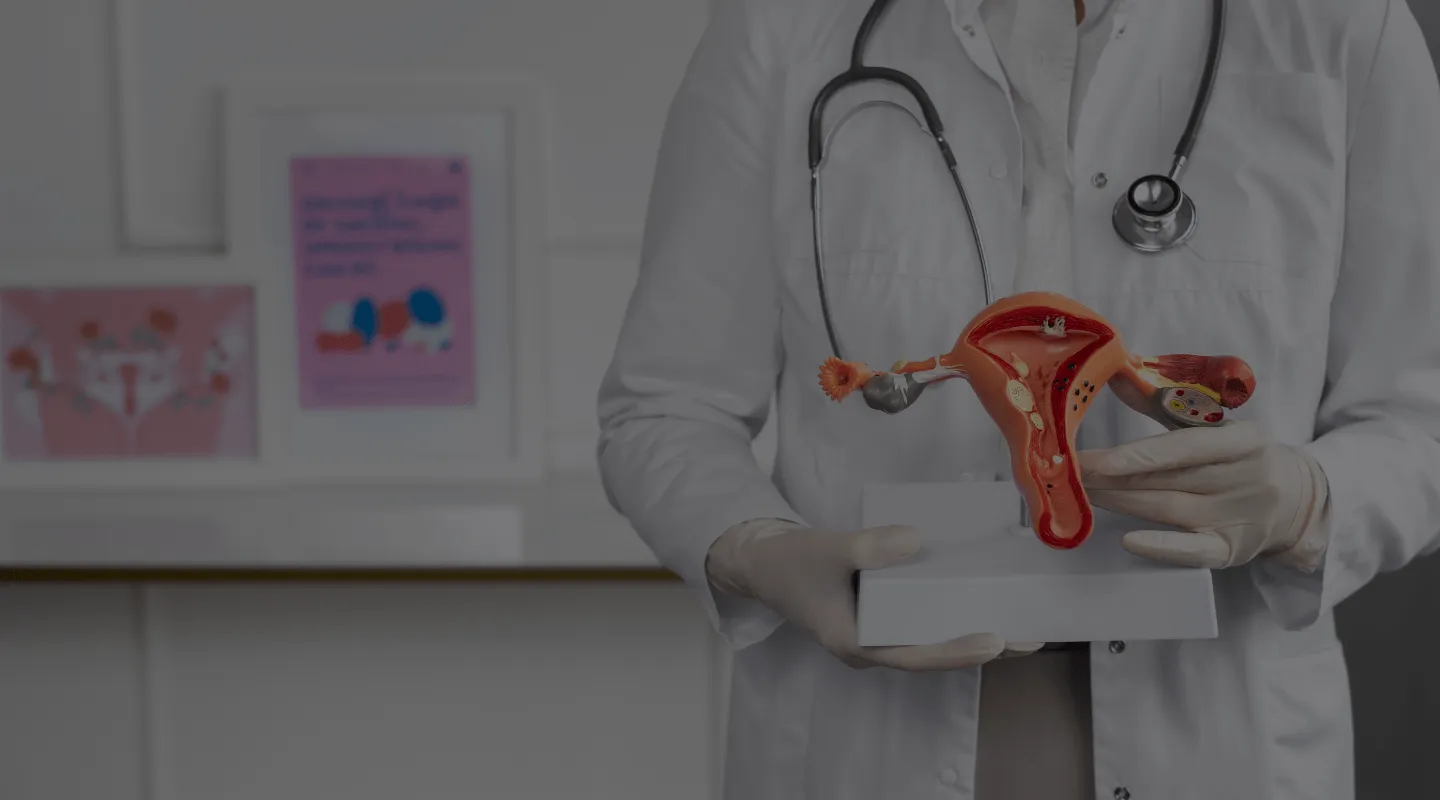
Ovarian Cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that can form in or on an ovary. Women have two ovaries, about the size and shape of an almond. Eggs that develop and mature in the ovaries are released in monthly cycles during the childbearing years. Many women have ovarian cysts that appear and develop over time. Most ovarian cysts do not interfere with daily life and are harmless. Moreover, the majority disappear without treatment after only a few months. However, ruptured ovarian cysts can cause serious symptoms. This is why regular check-ups and pelvic ultrasounds are necessary to detect cysts.
What are the symptoms of an ovarian cyst?
Most cysts show no symptoms and disappear on their own. However, if the ovarian cyst is large, it may cause:
- pelvic pain,
- lower abdominal pain on the side of the cyst,
- a heaviness in your abdomen,
- bloating.
Complications of an ovarian cyst
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled formation that develops on or in one or both ovaries. While most ovarian cysts are benign and cause no symptoms, some can cause complications. When an ovarian cyst grows, it can put pressure on surrounding organs, such as the bladder or rectum, which can cause pain and discomfort. In some cases, the cyst can twist the fallopian tube or ovary. This torsion can lead to intense pain and ovarian torsion. Ovarian torsion is a medical emergency and requires immediate surgical intervention to preserve ovarian function.
Another type of complication is the rupture of an ovarian cyst. When the cyst ruptures, its liquid contents spill into the abdominal cavity, which can cause intense abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. In some cases, the rupture of an ovarian cyst can lead to internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening. In the event of an ovarian cyst rupture, surgery may be necessary to stop the bleeding and remove the cyst.
Ovarian Cyst Diagnosis
The diagnosis of an ovarian cyst is an important medical process to recognize the presence of an abnormal mass in a woman’s ovaries. Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the ovaries, and they can be benign or malignant.
Here is a detailed overview of the different stages of ovarian cyst diagnosis:
Medical History and Physical Examination
The doctor will begin by gathering information about the patient’s medical history and symptoms, such as pelvic pain, abnormal bleeding, or changes in the menstrual cycle. Then, he or she will perform a physical examination to look for signs such as pain when palpating the abdomen or ovaries;
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging method that uses sound waves to produce images of internal organs, including the ovaries. Pelvic ultrasound is the most common technique for detecting ovarian cysts. It can help determine the size, shape, and nature of the cyst. It can also differentiate functional cysts, such as ovulation cysts, from pathological cysts, such as dermoid cysts;
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan
Computed tomography is an imaging method that uses X-rays to produce cross-sectional images of the body. It can be used to visualize ovarian cysts and to help determine their size, shape, and location;
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields to produce images of internal organs. It can be used to differentiate benign ovarian cysts from malignant cysts and to assess the presence of solid tissue in the cyst;
Tumor Markers
Tumor markers are substances produced by tumor cells that can be detected in the blood. Tumor markers are often used to monitor the evolution of ovarian cysts. For example, CA-125 is a tumor marker used to detect malignant ovarian cysts;
Classification of Ovarian Organic Tumors
- Serous tumors: Are the most common ovarian tumors. They are often malignant and develop from cells of the epithelium on the surface of the ovary. Endometrioid tumors are also malignant and form from cells resembling those of the uterine lining;
- Mucinous tumors: Are ovarian tumors that form from mucus-producing cells. Brenner tumors are rare, benign tumors that develop from cells of the epithelial tissue of the ovary. Clear cell tumors are malignant tumors that develop from cells resembling glandular-type cells;
- Mixed tumors: Are ovarian tumors that contain elements of different types of tissue. For example, stromal tumors are rare tumors that form from the supporting cells of the ovary. Granulosa, Sertoli, and Leydig cell tumors are rare tumors that develop from hormone-producing cells in the ovary;
- Germ cell tumors: Are ovarian tumors that develop from the germ cells of the ovary. They can be benign or malignant and include several subtypes, such as teratomas, yolk sac tumors, and mixed gonadal dysgenesis;
- Finally, connective tissue tumors are rare tumors that form from the connective tissue cells of the ovary.
Treatment of Ovarian Cysts
An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled mass that forms in one of a woman’s ovaries. There are two types of ovarian cysts: functional cysts and non-functional cysts.
Functional cysts are the most common and form when a follicle does not release an egg but continues to grow. Non-functional cysts, on the other hand, can be caused by a variety of factors, such as tumors or infections. The treatment of an ovarian cyst depends on several factors, including the size of the cyst, the age of the patient, and the presence or absence of symptoms. In many cases, functional cysts disappear on their own within a few weeks or months, without requiring treatment. However, if the cyst is large or if it causes symptoms such as pain or abnormal bleeding, treatment may be necessary.
Treatment for functional cysts may include hormone-regulating medications, such as oral contraceptives, or pain relievers. In more serious cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the cyst. However, most women recover fully after appropriate treatment and are able to lead normal lives. Hemorrhagic ovarian cysts are a variant of functional cysts, in which the cyst fills with blood. Symptoms may include sudden and intense abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. Treatment for hemorrhagic ovarian cysts often involves surgery to remove the cyst and prevent internal bleeding.
Duration of Ovariectomy
The duration of an ovariectomy varies depending on several factors:
- the type of surgery performed (open or laparoscopic),
- the complexity of the case,
- the surgeon’s experience.
Ovarian Cyst Surgery Price
Surgery to remove one or more ovarian cysts is offered from 800 eur. To receive a personalized quote with an affordable ovarian cyst price, please contact us. Tunisia Destination Santé can arrange airport-to-clinic transfers and plan your stay.
Your health, our priority.
Request your free quote.
Alternative Treatments
A hysterectomy is a surgical procedure that involves removing all or part of the uterus. It may be considered as an alternative treatment for ovarian cysts, particularly when they cause intense pain or pose risks of complications. While it is a radical solution, it may be necessary in cases where cysts are recurrent or associated with other gynecological conditions. A hysterectomy therefore makes it possible to eliminate the cysts while preventing the reappearance of new cysts. However, it requires careful consideration and discussion with a healthcare professional regarding the long-term consequences. In this sense, the stakes are not insignificant. Indeed, the cessation of menstruation and the impact on fertility must be taken into account.
What are the different types of ovarian cysts?
Functional Ovarian Cyst
Every month, your ovaries normally develop cyst-like structures called follicles. Follicles produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone and release an egg.
If a normal monthly follicle continues to grow, it’s known as a functional cyst. There are two types of functional cysts:
- Follicular cyst: Midway through your menstrual cycle, an egg bursts from its follicle and travels down the fallopian tube. A follicular cyst begins when the follicle doesn’t rupture or release its egg but continues to grow;
- Corpus luteum cyst: When a follicle releases its egg, it begins to produce estrogen and progesterone for conception. This follicle is now called the corpus luteum. Sometimes, fluid builds up inside the follicle, causing the corpus luteum to grow into a cyst.
Functional cysts are generally harmless, rarely cause pain, and often disappear on their own after two or three menstrual cycles.
Other Ovarian Cysts
Types of cysts not related to the normal functioning of your menstrual cycle include:
- Dermoid ovarian cysts form from embryonic cells and may contain tissues and. They are rarely cancerous;
- Cystadenomas: These develop on the surface of an ovary and can be filled with watery or mucous material;
- Endometriomas: These develop as a result of a condition in which endometrial uterine cells grow outside the uterus, endometriosis. Some of the tissue can therefore attach to the ovary and develop.
Dermoid cysts and cystadenomas can become large, causing the ovary to move. This increases the risk of a painful twisting of your ovary, called ovarian torsion. Ovarian torsion can also lead to a decrease or cessation of blood flow to the ovary.
Recovery After an Ovariectomy
Recovery after an ovariectomy requires special attention to promote optimal healing. In the first few days after the procedure, it is normal to experience pain and discomfort. These symptoms can usually be managed with pain relievers prescribed by the doctor. It is also recommended to rest and avoid strenuous physical activity for at least a few weeks to allow the tissues to heal properly.
Patients should also monitor for signs of infection (fever, redness, or drainage at the incision site). Regular medical follow-ups are essential to assess recovery, especially if both ovaries have been removed. A balanced diet and adequate hydration can also support the healing process, while allowing women to gradually resume their daily activities and regain their well-being.
Risks and Side Effects of Ovarian Cyst Surgery
Ovariectomy carries certain risks and side effects that must be considered. Potential complications include:
- bleeding,
- infections,
- damage to adjacent organs.
Our advantages


Contact and Quote Request for an Ovarian Cyst
If you want to organize your stay to treat your ovarian cyst, Tunisia Destination Santé can assist you during your medical stay from your arrival at the airport. Feel free to contact us to learn more about ovarian cysts.
—
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, some ovarian cysts can affect fertility, particularly endometriomas and cysts related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). They can interfere with ovulation and make conception more difficult.
While rare, it is possible for ovarian cysts to develop after menopause. The majority of these cysts are benign, but the risk of cancer is higher, requiring careful monitoring.
Yes, certain genetic conditions, such as Lynch syndrome or Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, can increase the risk of developing ovarian cysts and other gynecological abnormalities.
Yes, large ovarian cysts can put pressure on the intestines and bladder, leading to symptoms such as bloating, constipation, and frequent urination.
Yes, ovarian cysts can cause menstrual irregularities, including painful periods, heavy bleeding, and bleeding between periods.
Signs of a ruptured ovarian cyst include sudden and intense abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, nausea and vomiting, and in some cases, fainting or dizziness.
Most ovarian cysts are benign, but certain types, such as cystadenomas or endometriomas, can have malignant potential, especially in postmenopausal women.
Natural treatments include dietary changes, supplements such as chasteberry (vitex), and stress-reduction techniques such as yoga and acupuncture. However, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional before starting any natural treatment.
In adolescents, ovarian cysts are often diagnosed by pelvic ultrasound due to abdominal pain or menstrual irregularities. Functional cysts are common and usually benign at this age.
Yes, hormonal contraceptives, especially birth control pills, can help prevent the formation of functional ovarian cysts by inhibiting ovulation.
