PRP Injections and Osteoarthritis
Thanks to its regenerative effect, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is no longer reserved for athletes. It is now used in other purely aesthetic procedures, such as hair transplantation and lifting, as well as in medical applications, including orthopedic surgery. Recently, the PRP injection technique has proven its effectiveness in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis (gonarthrosis).
What can be treated with PRP?
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is used to treat a variety of medical and aesthetic conditions. In regenerative medicine, it is commonly used to promote the healing of sports injuries such as sprains, tendinitis, and muscle tears. In addition, PRP is effective in treating male and female baldness, stimulating hair regrowth. In cosmetics, it is used to improve skin texture, reduce wrinkles, and restore facial radiance. This natural approach uses the body's own healing capabilities, often offering promising results without the risks associated with other more invasive treatments.
EXPRESS QUOTE
For more information
Your health, our priority.
Request your free quote
PRP injections for treating tendon injuries (tendinitis or tendinopathy)
Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) have become a promising method for treating tendon injuries such as tendinitis and tendinopathy. Using the patient's own blood, enriched with growth factors and platelets, this technique aims to stimulate the healing and regeneration of damaged tissues. PRP is injected directly into the affected area, which helps reduce inflammation, promote healing, and strengthen the tendon structure. This non-surgical treatment is often chosen for its ability to deliver significant results by reducing pain and improving tendon function, allowing for rapid and lasting recovery for many patients.
PRP injections for treating muscle injuries
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) injections are increasingly used to treat muscle injuries, offering a regenerative and non-invasive approach. By injecting PRP directly into the injured area, this technique uses the body's natural healing properties to promote the repair of damaged muscle fibers. The growth factors and cytokines present in PRP help reduce inflammation, stimulate the formation of new muscle tissue, and accelerate the recovery process. This method is often chosen for its ability to improve healing, reduce muscle pain, and restore normal muscle strength and function, allowing patients to regain their mobility and physical activity more quickly.
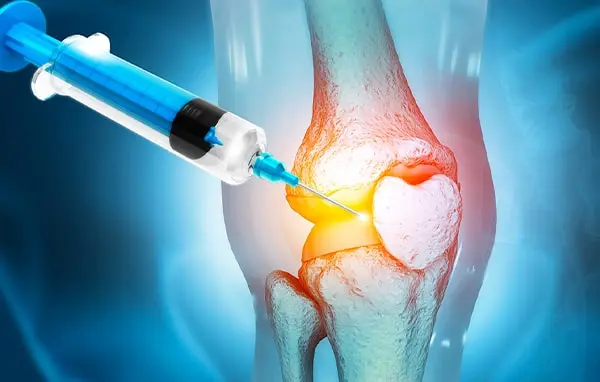
PRP injection in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis
PRP injections offer a promising option for the regeneration of damaged cartilage, the tissue covering the articular bones. This plasma liquid contains growth factors and bioactive molecules that can repair the tissues of the knee, hip, shoulder, or hand cartilage. Once injected into the affected joint, PRP promotes the production of the cartilaginous Extra Cellular Matrix (ECM) by chondrocytes. A division (mitosis) of these stimulates the growth of cartilage pieces. In addition, these plasma injections stimulate the development of blood vessels from those already existing. Subsequently, the PRP technique inhibits inflammation to reduce pain and improve joint function.
Procedure of the injection
First, the doctor draws a small amount of blood by inserting a needle into a vein in the arm. Then, he places the sample in a centrifuge to separate the components. Only the platelet-rich plasma will be used for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
In a second step, the doctor injects the collected solution into the affected knee joint space. He uses ultrasound to guide the injection and ensure that the plasma reaches the targeted areas. Pain and stiffness may occur after the injection, so it is recommended to arrange for assistance for the return home.
Mechanisms of action of PRP
PRP, derived from the patient's autologous blood, aims to restore the cartilage of the knee, or even the hip, through several mechanisms, including:
- Activation of dormant stem cells: PRP stimulates dormant stem cells in the injured area, promoting the regeneration of cartilage and surrounding tissues.
- Healing: The anti-inflammatory proteins in PRP treat tendon and ligament injuries by stimulating collagen synthesis.
- Lubrication: Platelet-Rich Plasma helps reduce friction, improve joint lubrication, and increase joint mobility.
Advantages of PRP injections in the treatment of gonarthrosis
As a promising treatment, PRP injections harness the body's natural healing mechanisms to alleviate discomfort, improve joint mobility, and slow the progression of knee osteoarthritis. Using the patient's own platelets, these injections are considered safe, with a low risk of side effects. In addition, this inexpensive technique is preferred by many doctors because of its simplicity: it involves the preparation and injection of the liquid directly into the inflamed joints. By promoting targeted cartilage regeneration, it offers an alternative to major surgery.
Post-procedure instructions
After platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, it is essential to maximize the effectiveness of the treatment and facilitate your body's healing process. To ensure good rehabilitation and prevent any complications, it is recommended to follow these instructions: